In the conditions of growing cucumbers over a large area in open ground, bushes may not be formed, but in the greenhouse this procedure is inevitable. Why do you need to do this and what are the advantages of the process? We will understand the article.
Why form cucumbers in a greenhouse?
The formation of cucumber lashes as they grow is necessary not only for growing a rich crop, but also for the appropriate use of the existing greenhouse space, which is required by almost every gardener. If this operation is not performed, then soon the bushes will grow over a large area and will become sloppy. In addition, with this size of the plant, the nutrients will be spent in significant quantities on essentially unnecessary shoots, which means that the fruits will develop slowly and at the end of ripening will lose their inherent taste.
- Other benefits of bushes are:
- the location of the lashes in such a way that the most suitable lighting mode is formed for the plant (lack of shade due to other lashes) and humidity (moistening occurs simultaneously and equally);
- vertical arrangement of bushes facilitates maintenance procedures (watering, weeding, fertilizing, spraying), as well as harvesting;
- pinching significantly increases the fruiting time.
Video: How to shape cucumbers
Basic rules of formation
Each stage of the formation of bushes (garter, harvesting leaves and stepsons, as well as pinching) has its own implementation features. Consider them in more detail below.
Before planting cucumbers in the ground, it is advisable to choose a garter method, which will greatly facilitate the further formation of cucumber bushes.
Tying can be horizontal (along the bed), vertical (perpendicular to the landing) and combined:
- Horizontal garter method involves tightening between two or more vertically arranged metal or wooden high support structures of a strong rope (twine, twine, rope or cable) or wire in horizontal rows observing a distance of 25-30 cm. According to gardeners, such a garter is most convenient in low greenhouses, however it often happens that the antennae of the stems do not have time to reach the next tier and begin to weave horizontally.

- Vertical Garter - the most popular to use when planting the plant in question in a polycarbonate greenhouse. According to him, from the upper profile it is necessary to tie up vertical sheer trellises (2-3 cm wide) to the places located under the second leaves of each bush of the plant perpendicularly, making loops. As they grow, the stems wrap around strong and non-slippery twine (it is preferable to take jute).
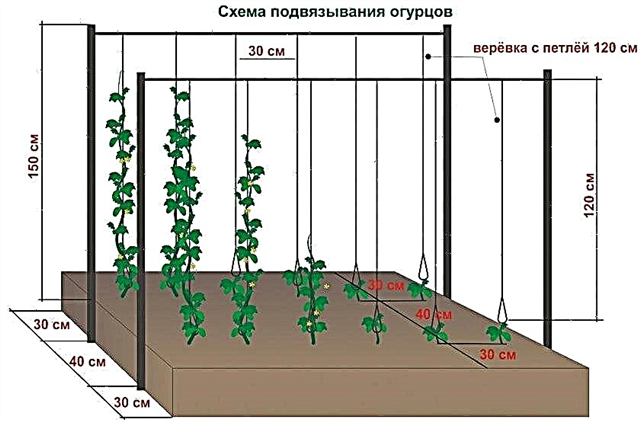
- Third method consists in pulling between the supporting structures of the grid and the formation of beds in separate small groups. Recently, a special cucumber net appeared on the agro-technical market, which is rapidly gaining popularity because of its convenience and the ability to replace vertical supports with itself. It is also possible to establish it by tilting, in the form of a so-called tent. According to gardeners, trauma to the stems and leaves of the plant with this method remains at a minimum level, and due to the excellent illumination of all parts of the plant, the yield is highest.

The main nuances taken into account when implementing a garter:
- if the grassy plant reaches the height of the first horizontally stretched twine, the stem must be carefully and freely, without pulling, tied to the support, and then wrap it around the rope, sending clockwise (as a rule, this is done every week);
- the top of the bush should be free to avoid yellowing;
- lateral processes should be tied to the central stalk or placed close to the angle of deviation no more than 30–35 °.
The leaves are harvested so that the extra ones do not consume food and water:
- below plants at a height of about 15–20 cm from the soil there should be no fresh, yellow or damaged or stumps from them - when watering, these are the first leaves that quickly deteriorate and interfere with the nutrition of others;
- removal must be carried out by trimming, but in no case breaking off.

Harvesting side stepsons, or stepsoning is done so that the yield comes faster thanks to a larger number of female inflorescences:
- lateral shoots no larger than 3-5 cm in size must be removed, as a rule, at the same moment as the first leaves of the plant;
- Be attentive to those varieties in which the formation of female inflorescences occurs precisely on the shoots, and not on the stems. If you inaccurately perform this procedure, you can lose the future crop of the plant.
Important! Later harvesting of the lateral stepsons (when they crossed the 5 cm length) adversely affects the development of the herbaceous plant.
When performing the correct formation of bushes, the latter have the form of an inverted isosceles figure of a triangle. Thus, an increase in the load on the central main stem occurs gradually, and the lower lashes are well ventilated and less susceptible to disease. At the same time, it is necessary to remove the ripened fruits sequentially, without waiting until everything is ripened: fewer fruits do not load the cucumber vine.

How to properly form cucumbers in a greenhouse: a step-by-step guide
In connection with the presence of various varieties of the described plant, there are various ways of its formation, which we will analyze below.
Parthenocarpic varieties
Partenocarpic variety of cucumber - this is such a variety of plants that are able to form new fruits without pollination. And since they do not need to be fertilized with insects, it is possible to form an ovary to get an excellent crop by pinching and regularly adjusting the density of the bush. Such varieties are famous for the rapid build-up of young shoots, which must be controlled by the formation of bushes.
Learn more about the variety of parthenocarpic varieties of cucumbers:
For these plant varieties, the shape of the bush does not play the most important role, in contrast to the amount of light falling on the stems. The lateral processes are characterized by a high level of branching, so it is preferable to grow them in the form of a single vine on a trellis, that is, in a single stem.
The formation is as follows:
- The main stem, after it forms 4-5 leaves, is tied to a trellis support.
- When they reach a height of 40-50 cm, the lateral processes are removed (no more than 5 cm in length). Performing this action too late will result in the plant dropping already formed ovaries.
- Further shoots must be left in three tiers:
- about 1 m from the soil - processes up to 20 cm;
- more than 1 m from the ground - processes of 40 cm;
- more than 1.5 m from the ground - processes of 50 cm.
Video: How to properly form bushes of parthenocarpic hybrids of cucumber in a greenhouse
The tops must be clipped, and thus, we will have several leaves and one fruit on the first tier, several leaves and two fruits on the second, several leaves and three fruits on the last.
If the lash of the main shoot extends beyond the height at which the wire is installed, it must be wrapped around the trellis and nibbled, or it should hang down freely and further nibble near the soil itself.
Did you know? In the city of Nizhyn, Chernihiv region (Ukraine), a monument to cucumber was erected, the official opening of which was carried out in 2005. The pedestal is a huge granite barrel with a cucumber lying on its lid, which was erected in honor of the local canned vegetables TM "Nezhin".
Bee pollinated and branched varieties
The ovary in the above varieties of cucumber is formed only after pollination by insects. Growing them with one stalk is inefficient, although it is possible in greenhouse conditions. The frequent absence of the desired result is explained by the arrangement of the female genus with flowers mainly on the side shoots, and not on the main stem, where there are more male inflorescences. Bushes of branched species of cucumber, as well as bee pollinated varieties are formed according to a multi-stem structure. The main stem is pinched at the level of 4-6 leaves, and preferably above it in order to form new processes.
Bee pollinated cucumber varieties include:
The key principles in the pattern of formation of bee pollinated and branched varieties of cucumber are the following:
- the main stem is tied to the trellis when it has already formed 4-5 leaves. The lateral processes in this case do not touch until the first ovary is formed on them;
- as soon as the first ovary appears on the lateral shoots, they must be tied to adjacent trellises or pulled higher to the main stem, observing the angle between them of 60 ° or more;
- an alternative option for tying the side shoots is twisting around the main stem;
- the specified operation must be repeated regularly, periodically removing unnecessary and interfering shoots and antennae;
- after whipping the central shoot outgrows the height of the wire garter, the shoot must be wrapped several times in free order around the trellis, pinching the crown;
- at the end of the vegetative process, patients, as well as shoots that are not ovary, must be removed.
Video: Formation of bee pollinated cucumbers in a greenhouse
If the varieties of cucumbers are not self-pollinated, then at the stage of bud formation, it is necessary to open the windows and doors of the greenhouse, as well as lure the bees to the flowers using sugar syrups or honey.
Important! In a horizontal garter, a rope or rope can also be pulled upright to facilitate the growth of bushes. The supports should be high so that the upper tiers of the plant do not obscure or cover the lower ones.
Extra care for cucumbers in the greenhouse
Just forming a bush for active growth and optimal development of the plant is not enough, so let's look at additional principles for caring for cucumbers when growing vegetables in greenhouse conditions.
Optimal growing conditions
The main criterion for determining a suitable soil is its friability, which contributes to a greater saturation of the plant roots with oxygen (if the soil is clay, it is advisable to add sand or peat to it). Given the level of required acidity for cucumbers (pH 6–7), the best option would be to use a mixture of excrement of farm animals, sod-podzolic soil, humus and peat.
Checking the acidity of the soil in the greenhouse, where cucumbers are grown, should be carried out several times during the season: if it increases, a little wood ash should be added to the soil. In addition, it is advisable to carry out soil weeding and harvesting weeds.
It is very important to observe the microclimate in the greenhouse - it is better if you can adjust it:
- the first 7 days of growth, the air temperature should not be lower than + 20 ° C;
- during the second week - + 18 ... + 20 ° С;
- the stage of the appearance of the first fruits - + 22 ... + 24 ° C during the day, + 18 ° C at night;
- the humidity level should always be between 80 and 95%.
Watering and feeding
Watering and irrigation of cucumbers in the greenhouse must be carried out with cool or slightly warm water. In no case should you use icy or too hot water, as well as water the cucumbers with a hose. If the water is very cold, it is better to warm it in the sun and only after that proceed with watering. High pressure from the hose can damage too fragile stems and processes.
The best time to carry out the irrigation procedure is evening, about 18-19 hours.
The frequency depends on the period of plant development:- before the flowering process - A couple of times a day with a calculation of about 7-10 liters per 1 sq. m;
- after buds have formed - no more than once a day or even less.
During the growing season of cucumbers, fertilizer plants are usually carried out 5-6 times. The first time this is carried out using ammonia mixtures 14 days after the sprouts are planted in greenhouse soil. To increase the amount of deciduous mass, urea must be reintroduced as the plant grows.
The second feeding is carried out in order to protect cucumbers from all kinds of spring pests: under each of the bushes after pinching, you need to add a little wood ash. This element can generally be introduced at any stage of plant development, since it does not affect the quality of the fruit. However, in no case can you feed the upper parts of the bushes - this will scare off pollinators.
The third fertilizer is produced at the beginning of flowering in order to increase the number of buds, and, accordingly, the ovaries: 10 g of potassium sulfate is diluted in 10 l of water, and then bushes of cucumbers are poured in a moderate amount.
At a time when fruit development is observed, it is necessary to exclude nitrates and other substances that are harmful to the plant at this point. The best option would be to take peat and other organic mixtures (including humus, sawdust). Foliar feeding with ammonium nitrate is carried out urgently in case of a sharp drop in temperature in the greenhouse.
Important! In the process of pinching sinuses of leaves of bee pollinated and branched varieties of cucumber, the main point — Prevent blooming of flowers.
Ventilation
Elevated temperatures in the greenhouse can weaken the root systems of the bushes, as well as the penetration of fungal diseases. Therefore, in order to avoid stagnation of air in the greenhouse, as well as overheating of the plant, the greenhouse needs to be ventilated from time to time, it is best to use the upper windows.

Useful Tips
The procedure for forming cucumber bushes brings a more effective result, subject to certain recommendations:
- the first garter of plants to the trellis is made 2 weeks after planting cucumber seedlings in the greenhouse;
- the lower end of the twine should be skipped under 1 leaf of the stem, while the loop should be free, since with increasing liana the stem will gradually thicken;
- the garter should not be stretched - if the wire fluctuates, for example, from the wind, the stem can break out of the soil;
- at the level of each internode, as the stem grows, the lash is wound around clockwise;
- careful formation of the lashes of the plant, it is advisable to carry out within three months from the moment of planting;
- its implementation is most effective in the morning - the wounds on the stems heal before evening, and it is precisely at this time that there is less chance of infection of plants with infectious diseases;
- in the process of trimming, it is necessary to use only sharp scissors in order to achieve the most accurate and accurate cut, as well as the quickest healing of injured places;
- it is necessary to ensure that after trimming there are no stumps that contribute to the invasion of fungal diseases in the plant growth process;
- only the top part of the shoot is subject to systematic pinching - if you, for example, remove the stepson more than 10 cm, then injure the plant so much that at this moment its growth and development will simply stop;
- after the fruiting process begins on the lateral processes, the lash is pinched on two leaves weekly along with the removal of the tops of the shoots;
- in order to avoid damage to the stems, the latter must be carefully fixed;
- in the process of formation and collection of cucumbers, it is strictly forbidden to unfold the leaves and processes - as a result, they may turn yellow and stop their growth;
- after harvesting, the shoots from which it was harvested must be removed together with the cuttings.
Did you know? Watermelon and melon, as well as zucchini and squash, are relatives of the cucumber, since they are all from the Pumpkin family.
So, the formation of cucumber lashes in the greenhouse is one of the most effective techniques of agricultural technology, aimed at increasing the level of yield of cucumbers. By removing all unnecessary, you turn all the forces of the plant to the formation of fruits, and not the nutrition of the leaves, thereby controlling the pace of development of the vegetative and producing parts of the plant.















