Home apiary is an interesting sector of the economy, which can also generate income. Any business begins with training, and beekeeping is no exception. To figure out where to start and how to open an apiary, you need to study a large amount of information. About how to choose a place for hives, which hive to start with, how to choose and get bees, later in the article.
How to prepare for beekeeping
Beekeeping is a promising area of activity that over time turns into a profitable business. At first glance, breeding bees is easy, but organizing an apiary from scratch is a painstaking task that will take a lot of time and effort. First, settle the legal issues. You need to know the laws of your country on animal husbandry: in Russia, for example, permission to get bee breeding in half-wave is necessary. If you decide to get hives in the country, you should draw up all the documents in accordance with the law. Beginner beekeeper should understand the basics of beekeeping topics. To do this, read written manuals and lessons, articles by experienced beekeepers and peer reviews. The manuals of well-known apiologists, for example, Krivtsov N.I. and Kashkovsky V.G., will be useful. After acquiring basic knowledge, you can start working.
If you decide to get hives in the country, you should draw up all the documents in accordance with the law. Beginner beekeeper should understand the basics of beekeeping topics. To do this, read written manuals and lessons, articles by experienced beekeepers and peer reviews. The manuals of well-known apiologists, for example, Krivtsov N.I. and Kashkovsky V.G., will be useful. After acquiring basic knowledge, you can start working.
If you write down a step-by-step instruction on how to become a beekeeper, then you need to act in the following order:
- prepare a place for a new apiary;
- purchase equipment for protection, insect care and honey collection;
- choose and purchase the appropriate type of hives;
- buy a bee family.
Did you know? Historians call beekeeping the oldest type of beekeeping, or beekeeping on-board - breeding honey bees in tree hollows: until the 17th century, beekeepers used only this type in Russia.
How to choose a place for an apiary
The location of the hives is one of the key points in keeping bees. When choosing a location, pay attention to the following factors:
- The previous place of residence of the insects, from where they were transported after purchase, should be at least 5 km from the new apiary.
- Plantations where the bees will take pollen should be located a maximum of 1.5–2 km from the hive.
- You can not choose a place near roads or industrial enterprises.
- The carriageway, if it is nevertheless nearby, should not cross the path of insects to melliferous lands.
- The location of beehives along the path of bees from another apiary is considered erroneous.
- If it is decided to settle the bees near the house, the southeast side would be the best option.
- Choose a flat landscape - do not place hives on hills or in deep lowlands.
 Around the apiary should be planted, for example, hawthorn or acacia to create a hedge. Place the hive 3-4 meters apart, preferably in a checkerboard pattern. Given the recommended distance, you can calculate the apiary area in advance.
Around the apiary should be planted, for example, hawthorn or acacia to create a hedge. Place the hive 3-4 meters apart, preferably in a checkerboard pattern. Given the recommended distance, you can calculate the apiary area in advance.What beehives to choose for bees?
For hundreds of years of beekeeping, beekeepers have come up with many types of beehives. They are all different in design and have advantages and disadvantages. According to the basic classification, beehives are divided into the following types:
- single hull;
- double hull;
- multicase;
- sunbeds.
Important! When placing the apiary within a radius of 5 km from the place of purchase, the insects will return back to their old housing.
How to choose and purchase bees?
In the spring, maximum - in June, insects should be purchased. This season is optimal because bee families have broods of different ages. If it is not possible to buy a bee family in spring, you can make a purchase in the fall.
When buying a family, pay attention to the following factors:
- Breed. It is better to take a breed calm and adapted to your region. A good option is Carpathian bees.
- Quality uterus. The quality is indicated by brood of different ages, continuous sowing of eggs over the combs and the absence of laid queen cells.
- The power of the bee family. A strong family in the spring occupies 8–9 frames, in the summer - 14–15, and in the autumn –– 9–10.

Families buy packages. For an apiary without experience, optimal acquisition of 2–5 packets. Each package should have:
- 4-6 frames;
- 1.5 kg of honey bees;
- uterus;
- death to 20 individuals.
Leave the purchased bag overnight in the hives and cover with a insulated lid. In the morning, the bee family will live in new homes and begin work.
Useful equipment for the beginning beekeeper
The work of the beekeeper is impossible without proper equipment. It can be divided into three groups: protective accessories, care equipment and tools for working with bee products.
Did you know? In ancient Greece, images of bees were minted on coins.
Apiary protection
Beekeepers daily face the danger of bee stings. In large quantities, bee venom causes consequences - from allergies to death. In the event of a threat, insects secrete a fragrant secret, on which other members of the family flock, - the danger thus increases. That is why apiary owners use protective equipment. To protect the beekeepers put on a beekeeping suit. This is a set of clothes through which neither the insects themselves nor their stings pass.
The kit includes:
- overalls;
- gloves
- mask with a protective net.
Important! An inexperienced beekeeper should consult a veterinarian: a specialist will establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
What you need for proper care of bees
For competent care of the apiary, the owners acquire the following tools:
- Cell. Equipment for isolation of the uterus from other bees or its transportation.

- Feeder. Capacity for sugar syrup and top dressing, which is placed in the hive.

- Cap. The device for the capture of the uterus. With a cap, the uterus is also covered to rest on the comb.

- Drinking bowl. Capacity for water. The drinking bowl is installed either inside the hive or outside.

- Bee Remover. The device is used to free the honey body from honey bees. A bee eliminator allows insects to enter the nest housing and prevents them from returning. It is necessary for the successful selection of frames with honey.

- Separating grate. Used to block the passage of the uterus to another part of the hive.

- Royne. A device for collecting swarm bees for carrying. It has the form of a basket or box.

- Brush. With the help of a beekeeper, insects are removed from walls and honeycombs. Also, the equipment is used for cleaning in the hive - in particular, sweep the bottoms with a brush.

A set of tools for working with beekeeping products
Most apiary owners are interested in honey and beeswax. To work with products you must have the following tools:
- Beekeeping knives. Used for printing honeycombs. It is better to have several such knives.
- Honey extractor. A small machine for selecting honey from honeycombs without destroying them.
- Sump for honey. With its help, honey is cleaned of impurities.
- Equipment for mounting frames. It is necessary for attaching to the frames of all types of wax.
- Wax extraction equipment.
- Containers for storage of products.
How to care for bees throughout the year
To get honey, wax and other bee products, it’s not enough just to get an apiary: you have to take care of bees year-round. The owner must take into account the peculiarities of the development of the bee family, their nutrition, reproduction and the creation of honey by them. It is also important to know about bee diseases.
Features of the life of bees and care for them
The bee family is a matriarchal structure consisting of the uterus, working bees and drones. Each member of the family performs its functions.
The bee colony device is as follows:
- Uterus. The head of the bee family. The uterus produces offspring by laying eggs. Experienced beekeepers easily distinguish it from the rest of the family members - this is the largest insect with a pointed tail. Worker bees feed the uterus. Without the head of the family, the bee family cannot exist normally.
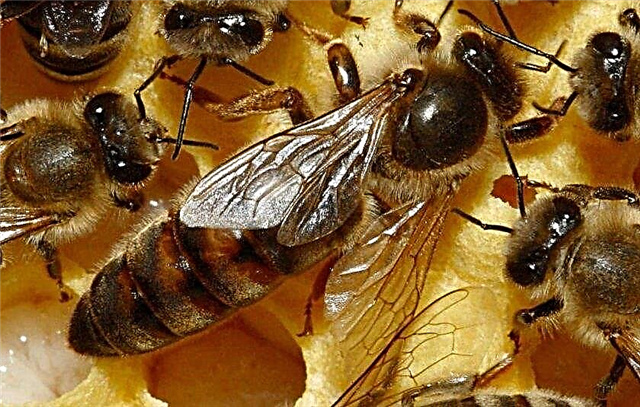

- Worker bees. This group of females settles the hive, feeds the remaining members of the family, collects nectar and produces honey. Worker bees are divided into two types: flying and beehives. Flying females are engaged in external work, collect nectar. Hive workers equip the hive from the inside.

- Drones. Males in a swarm act as an inseminator. They do not do any work, so before winter they are expelled from the family to cold death. Externally, they can be identified by a thicker back.

A quick guide to year-round family care is:
- Spring. At a temperature of + 8 ° C, the hives are exposed and transplanted by the bee family into a new dwelling.
- Summer. In June, bees are helped to swarm. By the end of August, store extensions should be removed and the condition of the hives checked.
- Fall. Beginning in the fall, beekeepers check the quality of honey. Mortar honey is pumped out of the cell and left to feed in the spring. It is better not to allow brood. The uterus is changed to a young one. The hive is prepared for wintering, collecting a bee's nest.
- Winter. In cold weather it is necessary to maintain darkness, temperature + 4 ° С and humidity 80%. Insects provide complete peace. Once a month, beekeepers clean tapeworms. A quiet noise comes from the hive during normal wintering. Loud buzzing and silence should equally alert the beekeeper.
Features of feeding bees
The bee family eats plant foods. Insects consume:
- nectar and pollen (mainly);
- fall;
- berry juice;
- fruit juice.

Bee breeding
Bees breed in two ways: laying eggs and swarming.
- Egg-laying. The uterus mates with drones a few kilometers from the apiary. Then she returns to the hive and lays eggs in her cells. Bee brood develops in four stages: eggs - larvae - pupae - bees. Eggs become larvae in three days - this is the stage of open brood. Further, the larvae turn into pupae. Pupation occurs by sealing the honeycomb. This is the closed brood stage. Young insects are born from pupae. A dense brood without missing cells speaks of a healthy uterus.
- Swarm. When there are many individuals, the bee family leaves the hive and is divided into two parts - this is its natural development. Apologists also developed a method of artificial swarming. The beekeeper should monitor the process and form the lay of the bee family. To control swarming, beekeepers use swarms, which are collected by the bee family.
How to get and save honey
Honey bees collect nectar from flowers. This is a raw material that is processed into honey. Bees pour nectar into the honeycomb cells located in the frame. When the honey matures, the cells are sealed. Honey is collected from the frame when it is 30% full. You can start a half-frame when there are 50% of the sealed cells in it.
To get honey:
- remove the frame from the hive and place it in the heat;
- meanwhile, heat a knife for printing honeycombs;
- cut off their lids and place the open frames in the honey extractor - the device unwinds them, honey flows out of the honeycomb and sinks to the bottom;
- Pour the finished honey through a sieve into a container. To preserve the product, it is better to choose a glass jar and tightly close it with a lid.
Store honey in a dark, dry place at room temperature.
Bee diseases
Bee diseases are divided into three groups: infectious, invasive and non-infectious. Infectious diseases develop due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the hive. Pathogens can be bacteria, viruses and fungi.
| Infection | Signs | Treatment |
| Ascospherosis, or calcareous brood | Drones larvae and insects up to 5 days old die. Corpses of insects are similar to fragments of lime of white or dark gray color. Adults do not die, but carry the infection, infecting the rest | Change the uterus, treat the hive with formaldehyde 5%, feed the insects “Asconazole” or “Mikoaskom” |
| Aspergillosis, or stone brood | Larvae and adults become stony, turn yellow and become black and white. | Relocate healthy insects to a different hive, and treat the infected one with formaldehyde 5%, feed the bees with Asconazole or Mikoaskom |
| Viral paralysis | In 1–1.5 weeks after infection, insects stop moving normally, become smooth and throw off the pile from the body | Move healthy bees to annual quarantine, burn infected hives, feed insects with sugar syrup with Oxytetracycline |
| Paratyphoid, or salmonellosis | Insect feces are liquid and smell bad | Feed the bee family “Streptomycin”, “Tetracycline” or “Biomycin” |
| Septicemia | Bees die, corpses crumble from touch | Move healthy individuals to quarantine and feed them with Chlortetracycline or Tetracycline. |
| European or American foulbrood | Some individuals weaken, change color or die. Corpses are brown, fetid | Relocate healthy insects to a new home, feed “Tetracycline” |
Invasive diseases get to the apiary in the infected inventory. An infected uterus can also transmit such a disease.
| Invasive disease | Signs | Treatment |
| Acarapidosis | Insects are affected by ticks. Symptoms are noticeable in the spring. The wings are twisted, the bees cannot fly up, bounce, pile together. Traces of diarrhea remain on the walls of the hive | Fumigate the hive with Teda. |
| Braulez | Lice no longer than 0.5 mm in length settle on insect bodies. Bees become restless | To process a beehive with smoke of "Phenothiazine" |
| Varroatosis | The appearance of ticks on adult insects and larvae. As they grow, ticks change color from light brown to brown. Pest attacks the apiary mainly in autumn | Withstand insects in heat chambers at a temperature of +40 ... + 48 ° С - under such conditions, ticks die. You can also use chemicals, for example, "Bipin" or "Phenothiazine" |
| Nosematosis | In sick bees, the abdomen swells, diarrhea begins, liquid stool remains on the walls of the house | Add Fumagillin to sugar syrup |
| Amoebiasis | Often appears as a secondary disease along with nosematosis. The belly increases, liquid feces remain on the walls of the hive | Treat with Fumagillin |
Non-communicable diseases are associated with a violation of the conditions in the apiary. They are conditionally divided into 3 groups.
Malnutrition:
| Disease | Cause |
| Carbohydrate dystrophy | Lack of feed |
| Protein starvation | Lack of pollen and pollen |
| Water starvation | Lack of drinking |
| Salt toxicosis | Mineral salt poisoning |
| Chemical toxicosis | Poisoning from plants treated with pesticides |
| Nectar and pollen toxicosis | Collecting nectar and pollen from poisonous flowers |
| Padova toxicosis | Mix paddy in honey |
Violation of the conditions:
| Disease | Cause |
| Caught brood | Subcooling Nests |
| Steaming | Lack of ventilation and high temperature |
| Dry sowing | Egg drying due to lack of bee-nurse |
Breeding Disorder:
| Disease | Cause |
| Sowing Sowing | Genetically diseased uterus that lays defective eggs |
| Frozen brood | The death of larvae due to prolonged family mixing |
| Body anomaly | Heredity, poor ecology |
| Grind | The uterus dies or does not lay eggs, and honey bees lay only unfertilized material |
Non-communicable diseases are treated with top dressing syrup and changing conditions. A novice beekeeper may make mistakes at the initial stage.
Experienced beekeepers call the following basic mistakes of beginner beekeepers:
- insufficient study of the foundations of the field in question
- incorrect location of the apiary;
- illiterate placement of hives;
- neglect of insect transport regulations;
- selection of aggressive breed;
- violation of conditions in the bee dwelling, unsanitary conditions;
- incorrect preparation of hives for frost.
Beekeeping cannot be a good new hobby for a summer resident, because bees need to be watched and looked after. Before purchasing the necessary tools for an apiary, be sure to learn all the secrets and subtleties of this area in order to understand from the very beginning how to become a good apiary, develop your business and make profit from bee products.