Yellow iris sounds in Latin - Iris pseudacorus. In the literal translation means "Iris pseudoair." The folk name of the plant is marsh iris, since this flower is easy to find near a river or in a wetland. The fact is that yellow iris is a hydrochorus and cannot spread on its own without water. This species feels great in urban areas and can grow in a country house with swamp land or some reservoir nearby, without any changes.
Grade description
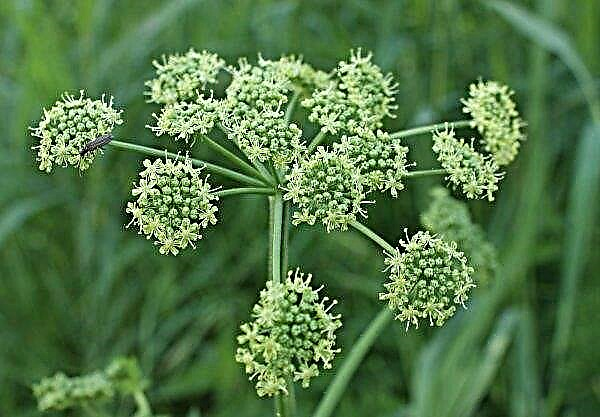
Stem Iris pseudacorus quite tall from 60 to 80 cm, has a branched shape and bears 12-15 flowers. A characteristic feature of this species is that when cut, the shoot quickly acquires a brown color. The upper petals of the iris flower have an underdeveloped appearance, the lower ones are large, golden yellow in color with a large orange circle in the middle. Rare representatives are white.
Did you know? Irises from ancient times are an integral part of the history of mankind. In Mesopotamia and Assyria they were considered a symbol of power, the Greeks named one of their goddesses by the name of this flower. — Irida, and our ancestors believed that irises grow in those places where the lightning of Perun fell.
Also, the leaves of the swamp iris have a characteristic feature - a sharply defined vein located in the center. Foliage changes its color from intense gray to dull green. There is a variegated form, which is considered decorative.
Swamp iris is a coastal and not an aquatic plant, although it can withstand prolonged flooding. It does not like dry soil, if drought occurs during the flowering period, there is a high probability of a decrease in the decorativeness of Iris pseudacorus.
Healing properties
A description of the healing properties of this plant can be found in any book on traditional medicine. Irises are used as expectorant and laxative medications. Decoctions of rhizomes help with indigestion, colitis, poisoning and gynecological problems.
Irises in the form of extract are included in many biological additives. In Tibet, irises are called “bu-shel-qi”. There they are used as one of the components of antiseptics and are included in the powder for sepsis and infections, which has external use.
Did you know? According to an ancient Greek legend, when Prometheus presented a flame to humanity, an incredible bright rainbow appeared on earth in honor of this. — all living things rejoiced in warmth. She shone all day and all night, and in the morning, where the rainbow sparkled, the first irises grew.
Growing Features
Growing yellow iris is not difficult. Its wild varieties grow well and multiply without the help of humans. The seeds of this plant are sown in the ground in autumn, to a depth of 1.6–2 cm, because during rains they can float up. The cultivated species can reproduce in separate pieces of rhizome, on which there are kidneys.
When growing Iris pseudacorus, do not forget about three important things:
- lighting;
- watering;
- top dressing.
 The flower does not like the bright sun, it needs a diffused light: ideally it should be a partial shade from some spreading tree. If in the garden where the swamp iris is planted, the soil is wet or marshy, then the plant does not need intensive watering. If the soil in which the flower grows dry, then it should be watered at least twice a week, especially if the iris was recently replanted.
The flower does not like the bright sun, it needs a diffused light: ideally it should be a partial shade from some spreading tree. If in the garden where the swamp iris is planted, the soil is wet or marshy, then the plant does not need intensive watering. If the soil in which the flower grows dry, then it should be watered at least twice a week, especially if the iris was recently replanted.
Marsh iris does not need special dressing, but just in case, once a year it can be fertilized with minerals, potassium and phosphorus (in a ratio of 1: 1 to 15 g per plant). Thanks to this, the plant will gain more magnificent forms. Feeding is best in September - October.
Landing rules
It is best to plant a swamp iris either in August or in September. The soil must be moist or watered. The land on which the landing is carried out must be protected from strong winds and illuminated by ambient light.
Important! At Iris pseudacorus has a certain feature: in the first year of growth, it sometimes shifts by 2-3 cm, and this should be taken into account when planning the landscape.
First, the roots can be grown in a container and then planted in a permanent place. The distance between the seedlings should be at least 40 cm, when planting dwarf species, a gap between them of 20-25 cm is allowed. If the gardener decided to plant the iris in the spring, then this should be done in April, when the growing season begins.
Before propagating the flower, it is worth fertilizing the soil with a potassium-phosphorus mixture or compost. Also, do not forget about the treatment of the site with fungicides and herbicides for disinfection. Watering, provided that the soil is dry, must be carried out immediately and 2 days after planting.

The subtleties of care
Caring for swamp iris does not require special labor costs.
The main thing is to follow certain rules and give the flower a minimum of attention:
- When the plant is located more than 20 m from the water, it is necessary to constantly ensure that the soil does not dry out.
- If severe frosts are expected, the flower should be transplanted into a deeper place.
- This culture has the property of rapid reproduction, if there is no desire to grow some irises, it is worth collecting its seeds.
- In winter, the leaves of the plant and its flowers should be pruned.
- To preserve the youth of irises, it is necessary to engage in their transplantation once every 5 years.

Pests and diseases
Iris pseudacorus, like all plants, is susceptible to a number of diseases.
There are "ailments" that are noted by gardeners as characteristic of this species:
- bacteriosis - It infects the root system of plants with harmful bacteria, causes rotting and softening of tissues. Turns a rhizome into a stinking liquid mass, leading to the fall of the entire stem.

- rhizoctonia - infection of the stem and roots of the fungus. Most often occurs in spring. Causes stalk decay in young irises and darkening of color, and soon drying out in adult plants. The spores of this fungus look like an oval, colorless stain. The mycelium, on the contrary, is dark brown and thick; the fungus spreads by contact.
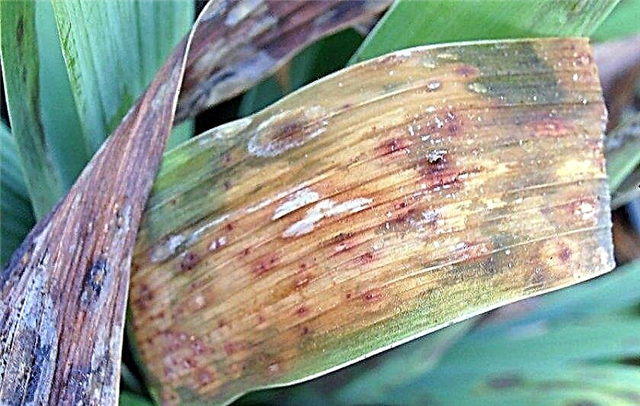

- fusarium rot - a fungus that infects tubers and stems up to a height of 20 cm. Appears when the soil is oversaturated with nitrogen or when the tubers are damaged. When it occurs, the rhizome is covered with gray-brown spots and begins to wrinkle. The disease can spread rapidly at positive temperatures.

- botritis - a mushroom that penetrates the root due to mechanical damage. Affected tissues become soft and turn brown. Subsequently, black sclerotia appears on the rhizome. It manifests itself when the soil is oversaturated with moisture.

- leaf spotting and rust - two types of fungus, harmful to the stems and leaves. On the affected areas, spots of gray-yellow hue appear. Soon they grab the entire leaf, which blackens and dries. If this disease is launched, then over time the plant dies.

- viroses - viral infectious diseases expressed by mosaics, deformations, chlorosis, growth inhibition, lead to the death of some parts of the flower or the whole plant. They arise due to the defeat of iris viroids, mycoplasmas and viruses. These diseases vary in biology, but are similar in effect. Transmitted through standard carriers - cicadas, aphids, bugs, ticks and thrips. A characteristic feature of the virosis is folds and wrinkles on the flowers, as well as a change in color to mottled or blurry-oily.
- functional diseases - appear in plants with unbalanced nutrition, when there is an excess or shortage of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other trace elements. They can be caused by high and low temperatures, metabolic disturbance and lack of oxygen in the soil.
Important! Most diseases of swamp iris can be avoided, provided that the proper cultivation and care of this plant is observed.
In addition to diseases, there is a list of pests that should not be allowed to yellow iris, these are:
- aphid;
- thrips;
- scoops;
- Bears
- nod;
- wireworms;
- chews and beetles;
- nematoids;
- slugs;
- flower fly.
Prevention of disease is primarily a constant care of the plant. It must be examined and, if stains or fungal infections are detected, treated with a 10% solution of bleach or hydrogen peroxide.
 Affected areas should be scraped and cut, sprinkling ash on the cleaned places.
Affected areas should be scraped and cut, sprinkling ash on the cleaned places.
Planting stock for prophylaxis is treated with a 5% solution of bicarbonate of soda or copper sulfate (0.1-0.2%). To combat insects, nothing better than treating plants with pesticides has not yet been invented. In addition, it is necessary to loosen the soil and remove weeds, which is a prevention against pests.
Iris in landscape design
Iris pseudacorus is often used in landscape design by artisans. Given the variety of yellow shades of this flower, it is combined with any kind of blue. And given his love of moist soil, he will feel great on the banks of a pond or artificial garden lake.
Flower beds, on which these plants are most, are called iridaria. Irises there grow in groups of 2-3 varieties selected for each other. In between, a “smooth” variety of iris is planted, after which the garden turns into a great place for walking.

In addition to the owners of iridaria themselves, in such flower beds an obligatory detail is water (fountain or pond), decorative stone and wrought iron garden furniture. There is a certain list of plants that are combined with swamp irises.

Of conifers, experienced designers recommend juniper, pyramidal spruce or thuja. Of the other representatives in the "modern" style, hosts, astilbe, geyhera, awl-shaped phlox and virgin tradescans will do.
Shades of spirea, rhododendrons and barberry shade yellow irises. Iris pseudacorus should be grouped around a tall plant in some geometric shape. On the borders, these flowers should be planted in small groups of 2-3 flowers.
Iris pseudacorus pleases the human eye since ancient times. This unpretentious plant can become an ornament in a cozy garden of a simple gardener and can decorate the park pond of the capital's garden.