Leeks have been cultivated since time immemorial. This vegetable was widely distributed in Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt. Over the millennia that have passed since its introduction into the culture, many varieties have been created, and farmers can choose a variety suitable for cultivation in their climatic zone. The article will discuss the characteristic features of varieties depending on the growing season and the specifics of cultivation of this useful vegetable, also known as pearl, or royal onion.
General characteristics of leek varieties
All varieties of this vegetable are divided into 3 groups, based on the growing season:
- early ripe (considered the most productive; growing season 3-4 months);
- mid-season (yield a crop of excellent quality; mature in 5-6 months after planting in the ground);
- late ripening (they are characterized by high resistance to weather conditions; harvesting is carried out 6-7 months after planting).
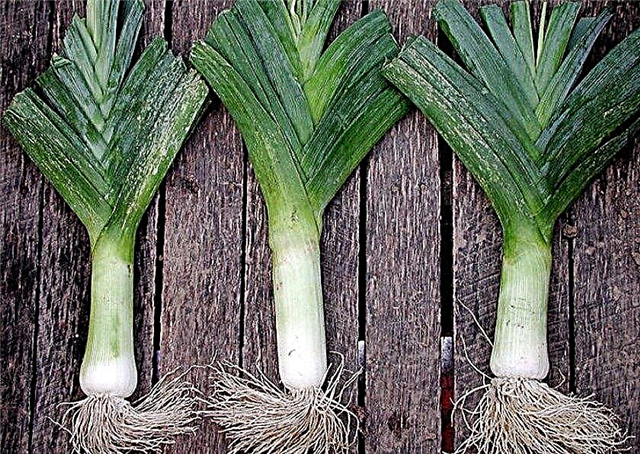

Onions of medium and late ripeness, in contrast to early ripening, are characterized by a tight fit of leaves to the stem. Mid-season and late leek are also suitable for wintering in the ground (in regions with a mild climate). A necessary condition is the presence of dense snow cover and a temperature not lower than –15 ° С. Autumn frosts are also not harmful to the harvest of these varieties, although they stop the further growth of onions.
Early varieties are distinguished by a length of up to one and a half meters, and a light green color of the leaves, whereas in the late leek, the stems are short, stocky and the leaves are darker in color.
Did you know? In Japan, leek is the most consumed vegetable. Its stems even serve as cutlery, used instead of chopsticks.
We select varieties taking into account the ripening period
In each group of varieties there are the most popular ones due to their high consumer properties and external parameters. Consider them later in the article.
Varieties of early ripening
They are also called summer. These varieties are very productive. It is their stems with a delicate, sweet taste that are most often used in dishes of French cuisine, in particular for the preparation of cold summer Vishisuaz soup.
Columbus
Ultra early Dutch variety. This is a powerful, resistant to cold plant, growing up to 80 cm in length. You can eat as much as 85 days after sowing. A pleasant feature for farmers is the absence of the tedious need to spud onions to get bleached pseudobulbs.
Vesta
Onion West with a characteristic high leg reaching 50 cm was bred at the Moscow Agricultural Academy a quarter of a century ago, and has since gained considerable popularity thanks to its spicy sweet-spicy taste, good resistance to diseases and cold, and excellent yield (up to 4-5 kg from 1 m²). Vesta matures 4 months after sowing. Plant height can be from 100 to 140 cm.

Elephant's trunk
It is characterized by dark green leaves, a fairly good yield (about 4 kg per 1 m²), a high-quality bleached stem 30 cm high and the ability to be stored for a long time, when placed in a sandbox.

Varieties of medium ripening speed
Mid-season leek is a plant with a dense, strong stem and large (up to 70 cm) leaves. It can be left to winter and in this case, with the arrival of heat, the onion will blossom and give seeds.
Casimir
Gives a crop 5 months after sowing. The plant is tall but compact. The leg reaches 30 cm in length.

Important! The leaves of Casimir are arranged almost vertically, which makes it possible to thicken the plantings, sparingly using the area of the garden.
Winner
Known not only for tasty bleached stalk, used both fresh and for preservation, but also for fragrant gray-green leaves, for the cultivation of which the Winner is left for the winter. It has excellent frost resistance.
Elephant
By maturity, the elephant is close to early varieties and ripens within 4.5 months after planting. Like the early leek, the elephant is able to grow up to one and a half meters in length. Unpretentious to moisture, frost-resistant, but needs thorough hilling. Elephant has dense, juicy stems about 20 cm long and blue-green leaves, sharp in taste.

Late Ripe Leeks
When cultivated in regions with a mild and temperate climate, this onion usually tolerates winter well, being in the beds under shelter. The false stem of these varieties is thickened and short.
Alligator
Grown both because of the stem, and to obtain fragrant herbs with a slight garlic flavor. The leg is quite large, as for later varieties, and reaches 30 cm. Alligator is also characterized by a good yield (up to 3.5 kg per 1 m²).
Quarantine
This is an old variety that appeared back in 1961 and has won the sympathy of gardeners due to its excellent taste, frost resistance and excellent keeping quality. Karantansky is distinguished by dark green leaves covered with a characteristic waxy coating.
Onion matures for a long time, about 6-7 months, although partial harvesting can begin as early as 4-5 months after sowing. It is better to plant it through seedlings, growing Karantansky from seeds is possible only in greenhouse conditions.

Bandit
Like most later varieties, the Dutch Bandit has a short leg, which, however, can be grown up to 30 cm by thoroughly hilling and mulching the soil. Also distinguished from other varieties are beautiful blue-green leaves. This onion can be planted later than standard time and left for the winter, harvesting in March.
Autumn giant
The onion lives up to its name, being powerful and tall (more than a meter), possessing large (up to 80 cm) foliage and unusual late varieties with a thick false stem reaching 40 cm. To obtain such characteristics, the Giant requires increased attention from the farmer: high hilling, high-quality top dressing, plenty of light and moisture.

Zoning Varieties
Starting to grow leeks, you should take into account the geographical features of your area and choose a variety in accordance with the climate and soil composition. Further, we will talk about leek, the most suitable for cultivation in the middle lane and harsh Siberian climate.
For central Russia
In the middle lane, in particular in the Moscow region, it makes sense to grow early and mid-season onions:
- Vesta;
- Casimir;
- Goliath;
- Columbus
- Elephant;
- Tango.
Over the long years of cultivation, the late-ripe Karantansky has also successfully established itself in the conditions of snowy, moderately frosty winters and quite warm, humid summers.
Novelties among hybrids (Pluston, Krypton, Mateyka), bred by breeders in 2017, are also ideal for growing in the middle lane.Important! In the regions of risky farming, it is not practical to grow late leek (with the exception of the specially developed Akreok variety), or it requires a heated greenhouse.
For Siberia
The best varieties for Siberia are early and medium:
- Vesta;
- Tango;
- Kilima;
- Columbus
- Jolant.
Leek Care
Being an ancient agricultural crop, leeks are at the same time little known to domestic farmers. The reason for this is the specificity of the climate and concerns about excessive labor costs during cultivation.
Consider the main agrotechnological techniques that will be required when cultivating leeks:
- He needs abundant watering 1-2 times a week. In rainy summers, this frequency is reduced, focusing on the state of the soil, avoiding waterlogging. Irrigation mode - 15–20 L of water per 1 m². Water should not be icy, but there is no need to defend it in the sun.
- To get a really tasty and juicy stem, the plant is fed. 3 weeks after planting - with mineral fertilizers (20 g of nitrogen fertilizer, for example, urea, and 10 g of potassium phosphate are diluted in 10 liters of water), and then organic fertilizing is applied once a month (infusion of cow and bird droppings).
- Together with top dressing, leek treatment with biological products is started to prevent infection by pests (for example, Fitosporin). During the onion fly, the garden should be covered with agrofiber.
- Regular weeding can be replaced by mulching the soil with straw, peat, sawdust.
- Leek requires loosening and hilling 2 times a month to obtain a strong, long, bleached stem.
Features of harvesting and storage of crops
The timing of the harvest depends on the characteristics of the variety. As already mentioned, the adult leek of middle and late ripening is not afraid of the first autumn frosts, so you can not rush too much with cleaning, conducting it in several stages and with knowledge of the following nuances:
- At the end of August - the first decade of September, selective cleaning takes place. Mature plants are being dug up that impede the growth of others, or those that no longer exactly grow to the parameters declared by the seed producer. An indicative sign of the onion's readiness for harvest is the presence of 4 wide leaves.

- Final cleaning is carried out before persistent frost, in late October - early November (depending on the region). Later varieties can be left for wintering, having hilled up to half the stem with soil or peat.
- Dig the leek gently using a pitchfork. After harvesting, the crop is left for several hours to dry in the fresh air (if there is no rain or snow).
Did you know? Leek roots can be cut off and left in the ground. They will be an excellent organic fertilizer.
Before laying for storage, the leek is sorted.
Small, non-standard plants can:
- dry in an oven or electric dryer;
- freeze, previously blanched and cut into pieces, and store in bags in the freezer.
Large plants can be stored for a long time (about 4-6 months) in the cellar (in sandboxes) or in the refrigerator (in bags with ventilation holes). Ideal conditions for storage - temperature 0 ° С and high humidity (about 80%).

Due to the variety of varieties, leeks can be grown in various conditions, including the harsh climate of Siberia. The article gave a brief overview of the most famous varieties of this vegetable and recommendations for its cultivation.